What Stabilizes The Secondary Structure Of A Protein
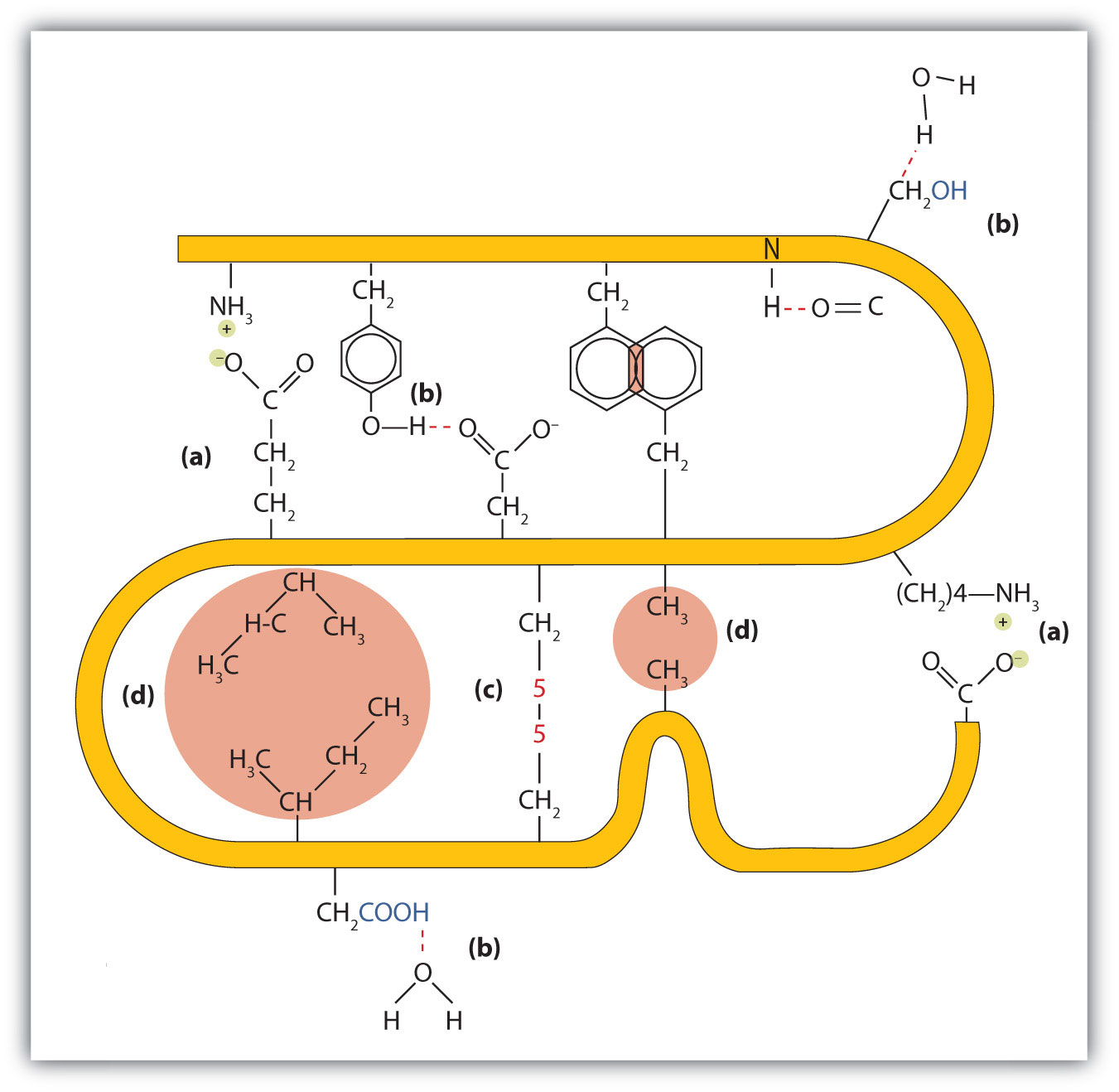
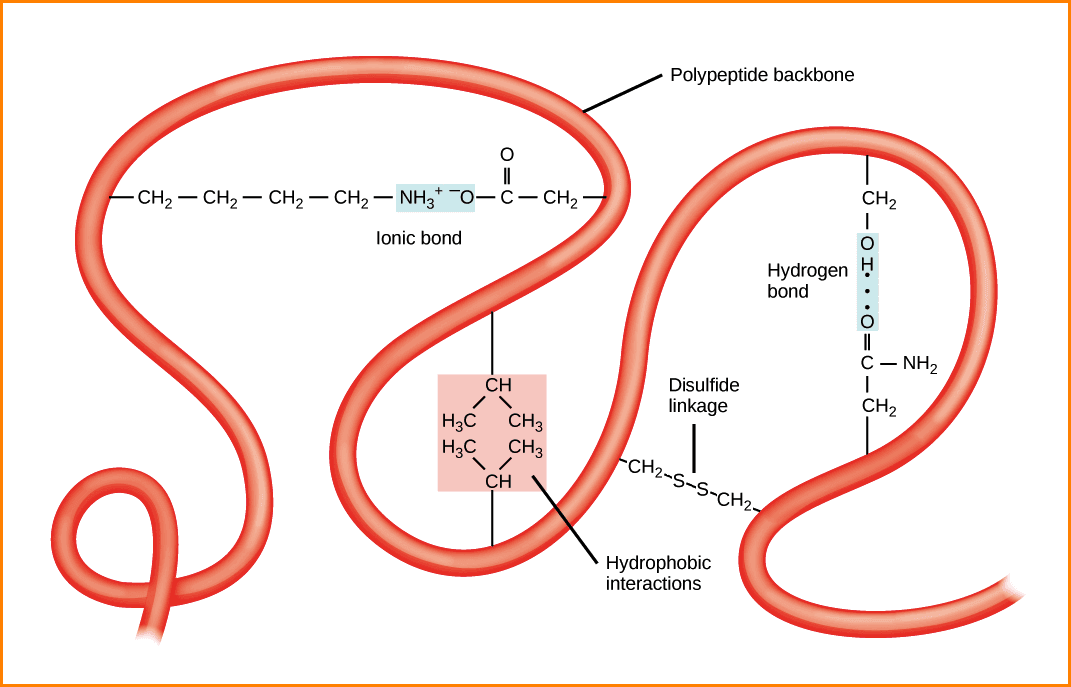
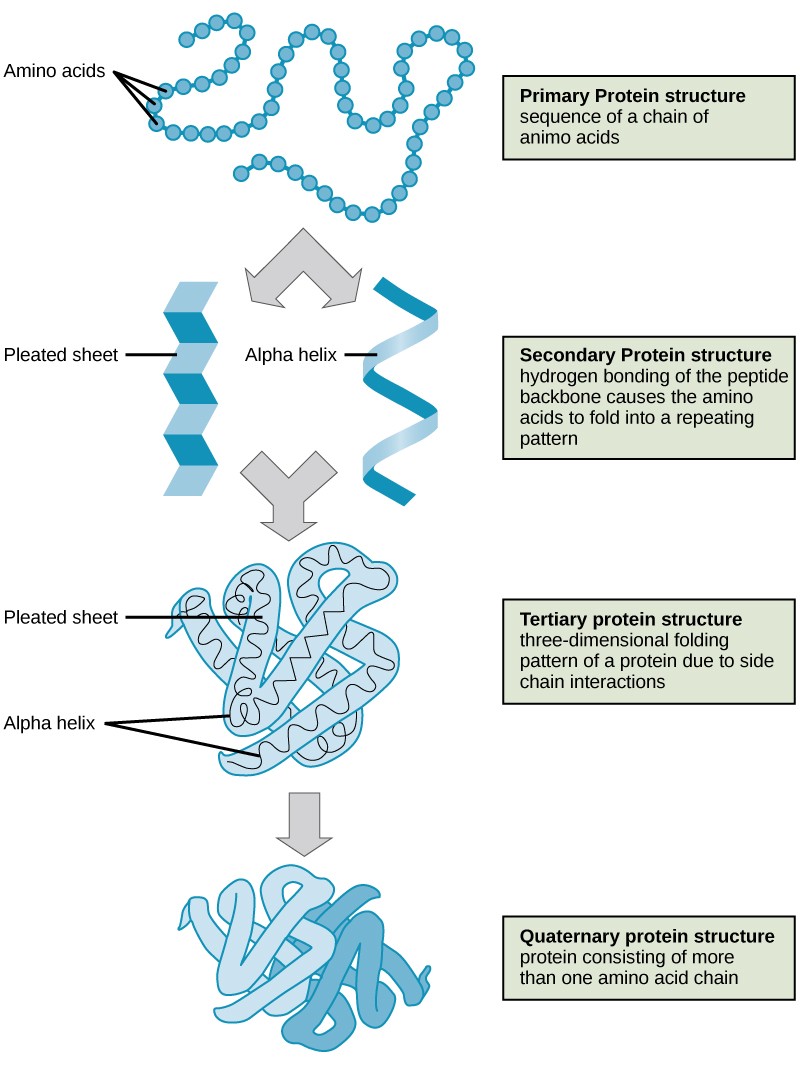
What Stabilizes The Secondary Structure Of A Protein - Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
12.Discuss the different kinds of interactions that stabilize the
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between.
Four Types of Protein Structure
Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary.
IB DP Biology HL复习笔记7.3.5 Levels of Protein Structure翰林国际教育
Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between.
UserEric Martz/Introduction to Structural Bioinformatics 2016
Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary.
Proteins Microbiology
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
Proteins
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
Protein Structure Drawing
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary.
Protein Structure Proteins are organized in tertiary Structure
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins Chemistry
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.
Chapter 3. Amino Acids & Proteins Introduction to Molecular and Cell
Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary.
Secondary Structure Elements Typically Spontaneously Form As An Intermediate Before The Protein Folds Into Its Three Dimensional Tertiary.
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds between. Secondary structures are those repetitive structures involving h bond between amide hs and carbonyl os in the protein backbone.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)