What Contaminates Annode At Discharge
What Contaminates Annode At Discharge - But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. However, anodes buried in clay soils. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually.
In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. However, anodes buried in clay soils. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig.
But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. However, anodes buried in clay soils. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually.
Sources of water pollution as freshwater contamination causes
Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. The anode, also known.
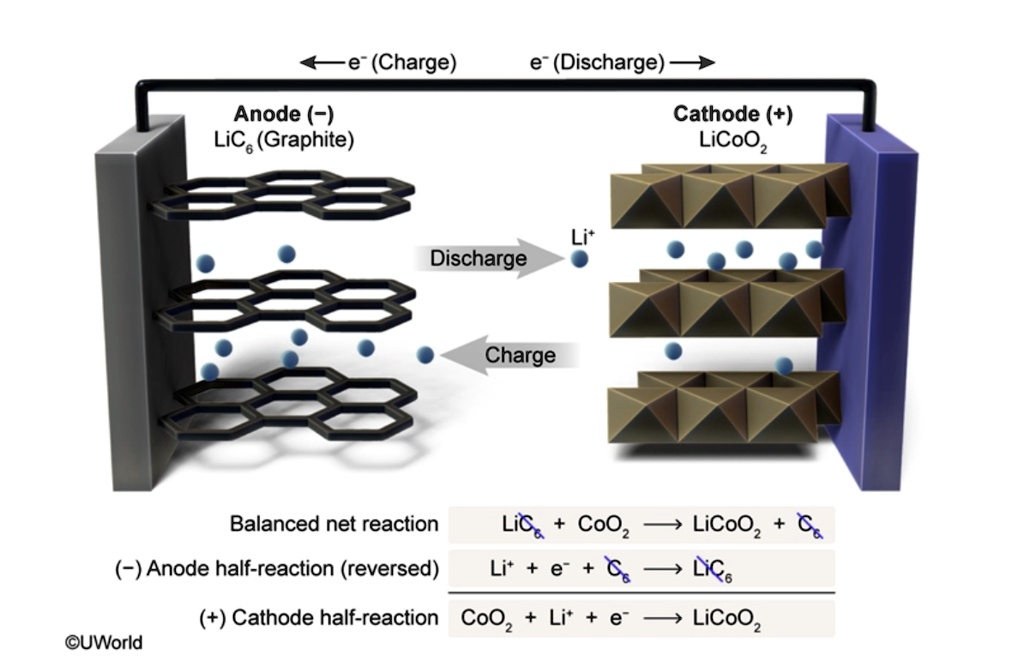
SOLVED (Charge) (Discharge) Anode ( ) Lics (Graphite) Cathode
In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. However, anodes buried in clay soils. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. Even a fully charged cell.
(a) Picture of the pin liquid anode discharge taken using a camera and
The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds,.
Chargedischarge profiles for first cycle of the Si anode in 1 M LiPF 6
In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. The anode, also known.
Principle setup of a battery cell with cathode, anode and separator
Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. However, anodes buried in clay soils. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on.
Typical visible changes occurring in the cathode and anode cells. The
But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. However, anodes buried in clay soils.
(a) Charge/discharge curve of an anode halfcell, with the anode behind
In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. However, anodes buried in.
Anode discharge VI characteristics for the UoSHHC and JPLHC 1
Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. However, anodes buried in clay soils. But increased discharge increases the growth.
Discharge curves of the investigated anodes (a) Mg6Al, (b
The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density. In addition, anion contaminates, such as f.
Table 1 from Investigation of the Effect of Anode Fuel Contaminants on
In addition, anion contaminates, such as f − from hf and pf 5, readily react with lithium to form insoluble reaction products. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. In free flowing water.
However, Anodes Buried In Clay Soils.
Even a fully charged cell deteriorates gradually. But increased discharge increases the growth of precipitates. The anode, also known as the negatively charged electrode, discharges lithium ions into the electrolyte as shown in fig. In free flowing water or in very wet soil ground beds, there is very little restriction on current density.