What Causes Metamorphic Rocks To Form From Existing Rocks
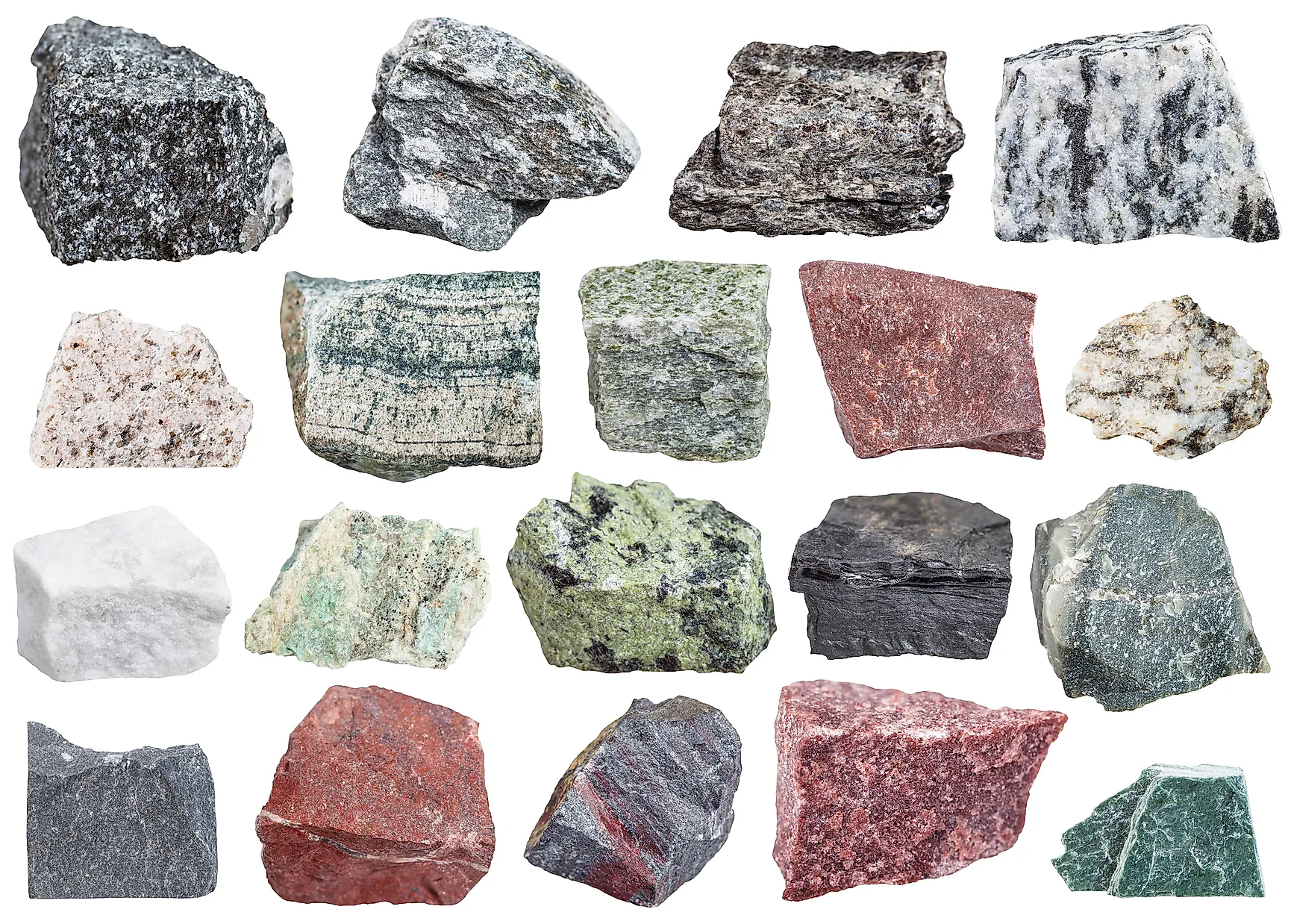
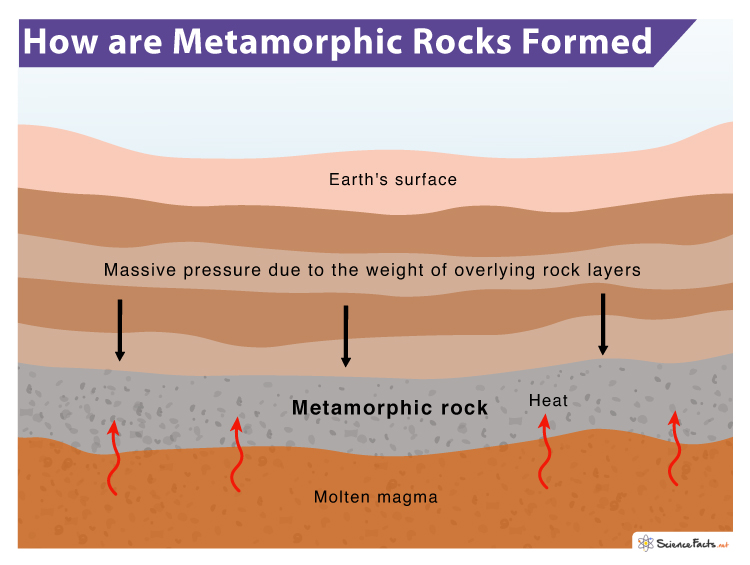
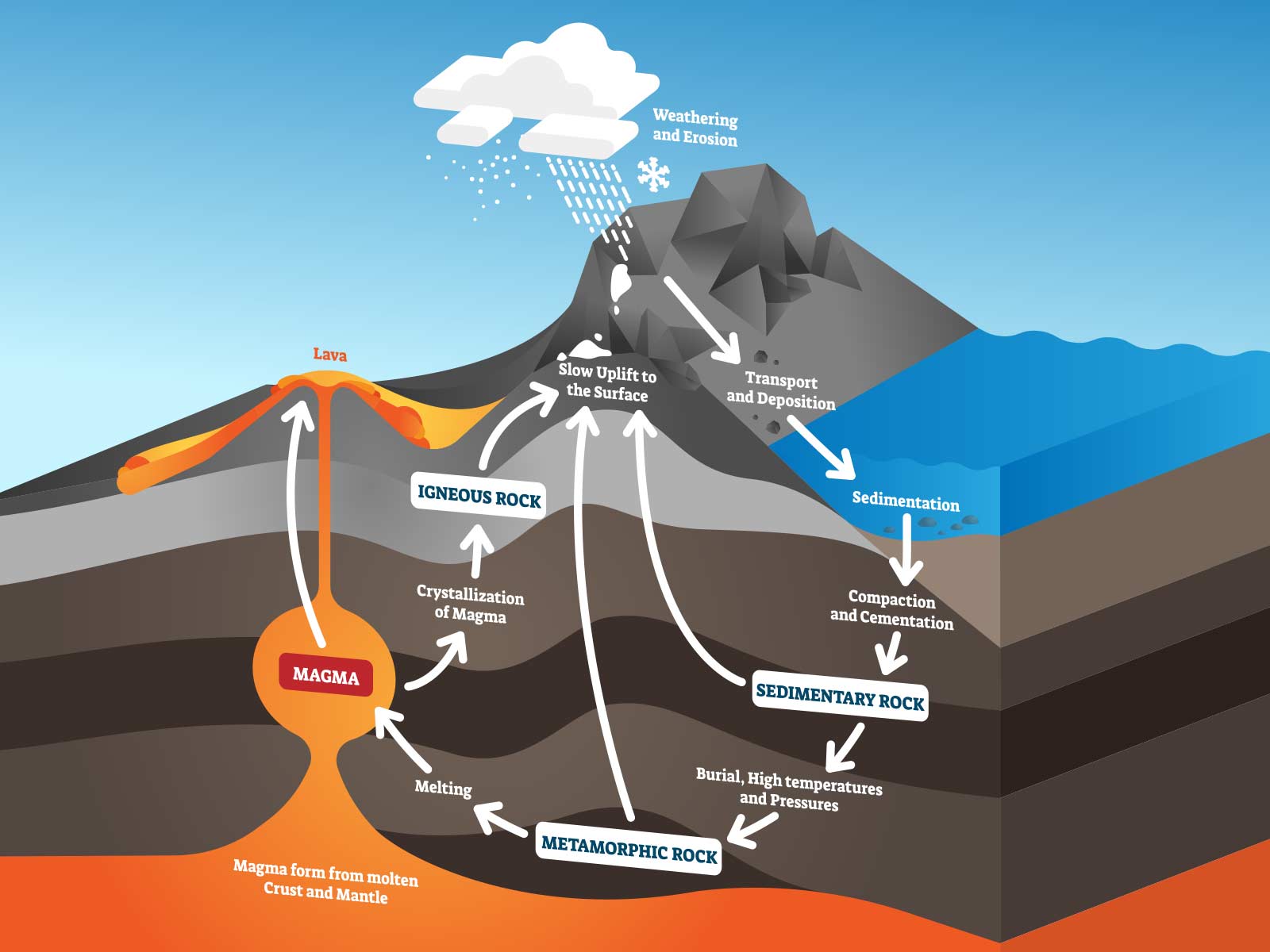
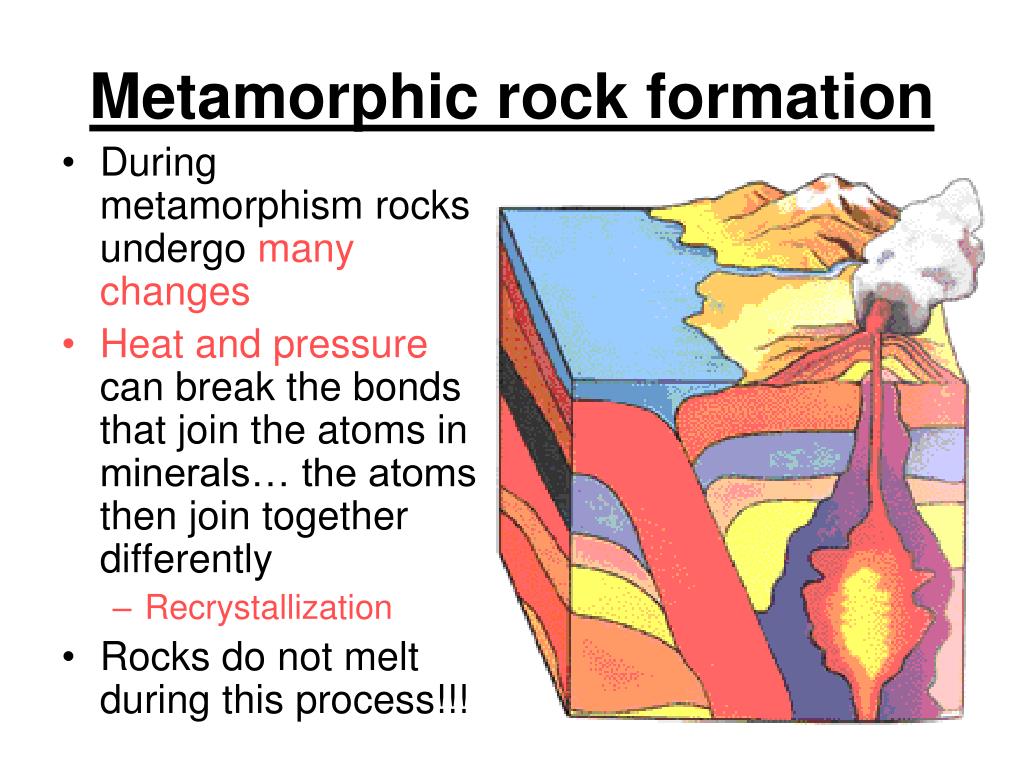
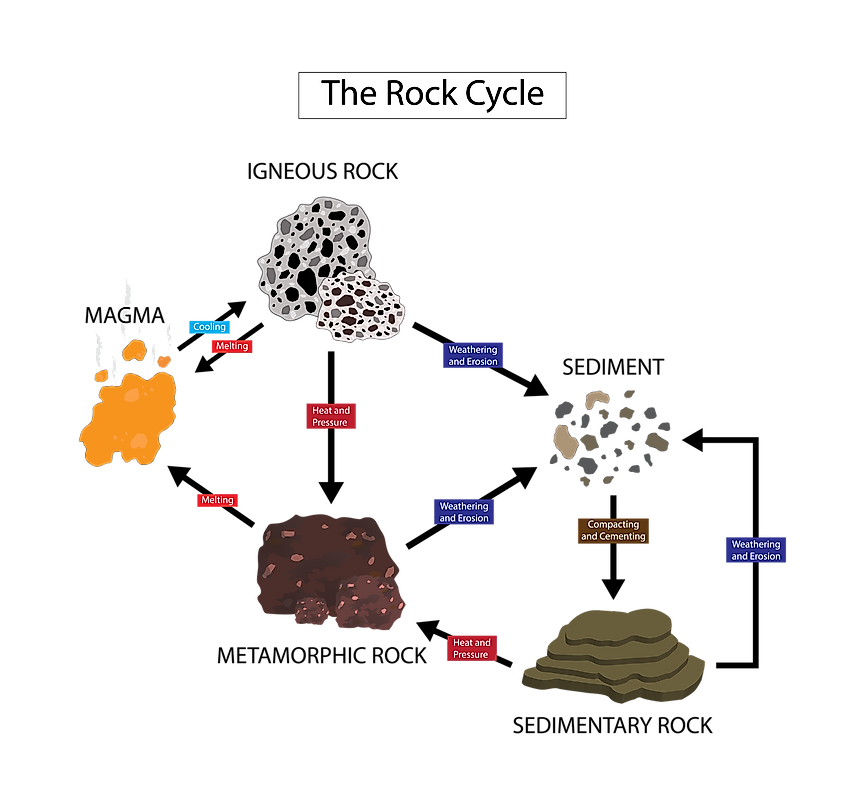
What Causes Metamorphic Rocks To Form From Existing Rocks - A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Pressure increases because of the weight of. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. Grains form in parallel layers. Examples include gneiss and slate. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks?
Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Pressure increases because of the weight of. Examples include gneiss and slate. Grains form in parallel layers. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks?
Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Grains form in parallel layers. Examples include gneiss and slate. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Pressure increases because of the weight of.
Metamorphic Rocks. ppt download
Pressure increases because of the weight of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. Examples include gneiss and slate. Grains form in parallel layers.
How Are Metamorphic Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Pressure increases because of the weight of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Examples include gneiss and slate. Grains form in parallel layers.
3.4 Metamorphic rocks form as existing rocks change ppt download
Examples include gneiss and slate. Grains form in parallel layers. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Pressure increases because of the weight of.
What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? O magma and
What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Pressure increases because of the weight of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Grains form in parallel layers. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of.
Metamorphic Rocks Definition, Formation, Types, & Examples
Grains form in parallel layers. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. Pressure increases because of the weight of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form.
Metamorphic Rocks Definition, Formation, Types, & Examples
Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Examples include gneiss and slate. Pressure increases because of the weight of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks?
√99以上 how do igneous rocks form into metamorphic rock 133365How are
Grains form in parallel layers. Pressure increases because of the weight of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks?
Metamorphic Rocks Pressure! Think Blue Marble
Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. Grains form in parallel layers. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Pressure increases because of the weight of.
Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. What causes metamorphic rocks to form from existing rocks? Grains form in parallel layers. Examples include gneiss and slate.
Which Statement Describes Metamorphic Rock Formation AndrewhasYoder
Examples include gneiss and slate. Grains form in parallel layers. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Pressure increases because of the weight of.
What Causes Metamorphic Rocks To Form From Existing Rocks?
A phenomenon called burial pressure causes metamorphic rock to form. Pressure increases because of the weight of. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing parent rocks are transformed (metamorphosed) by heat and pressure deep below the surface of. Examples include gneiss and slate.