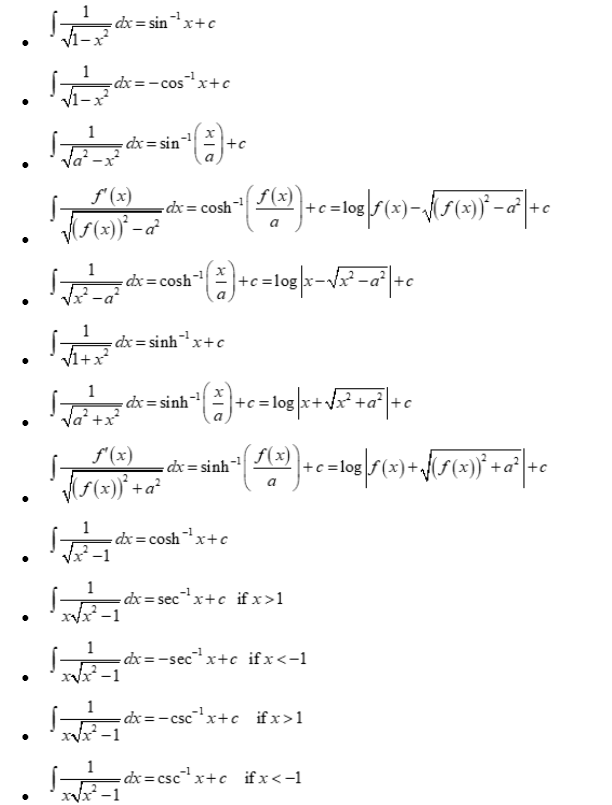Integral Rules Sheet
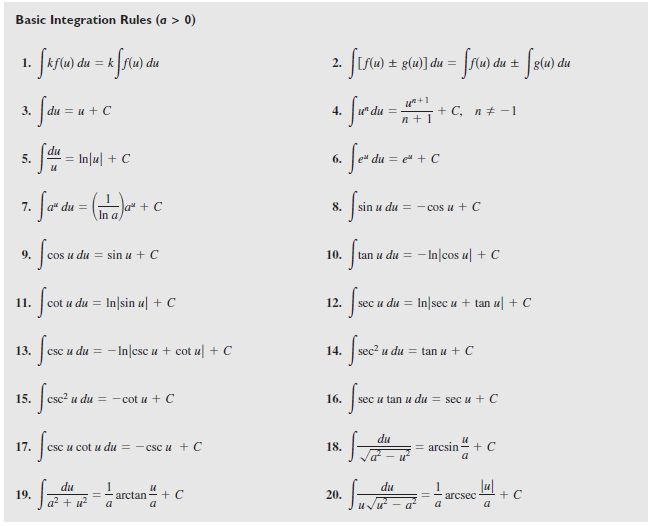
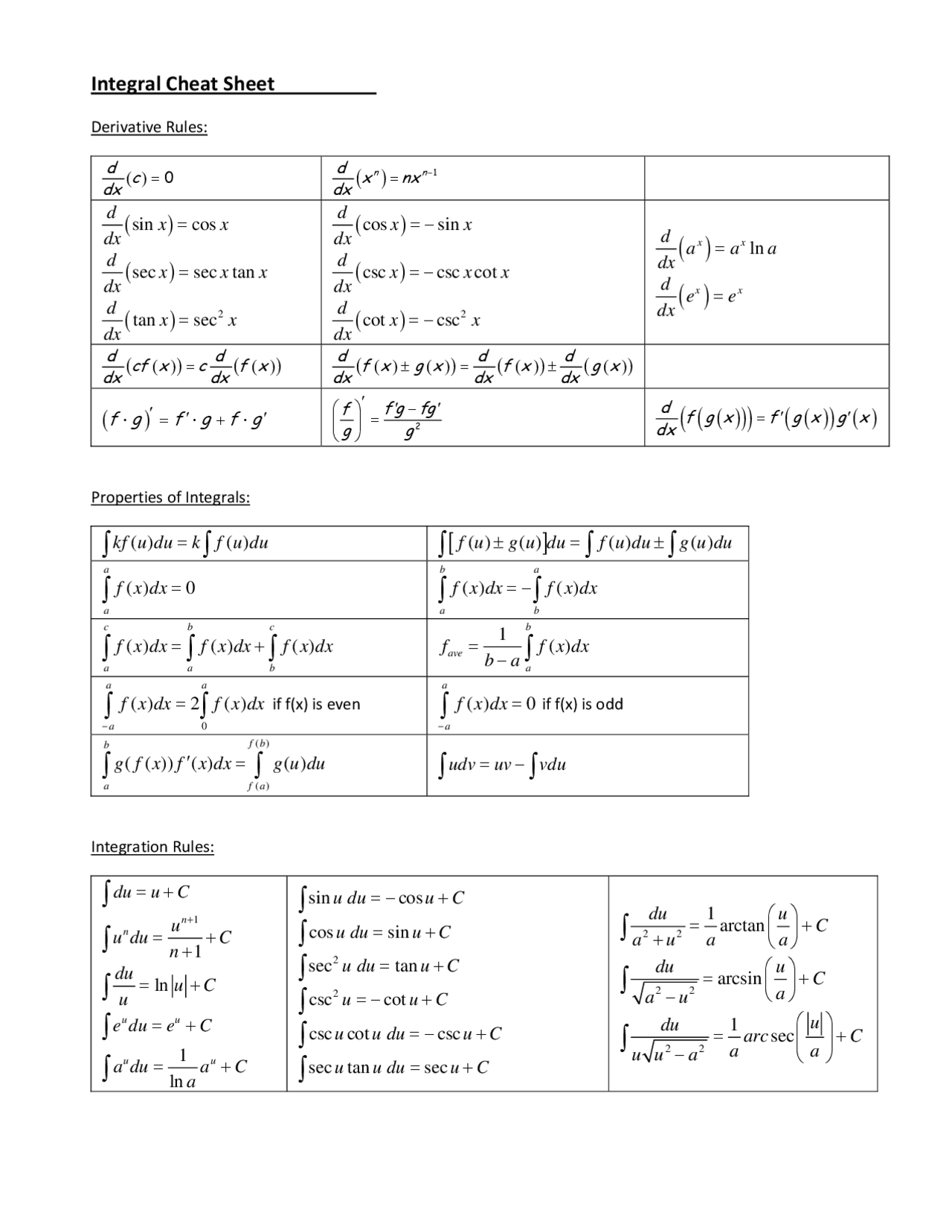
Integral Rules Sheet - Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2;
Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out:
( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Cheat sheet for integrals 1.
Page 1 of 2 Some Important Rules Of Differential & Integral Calculus
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value.
Basic Rules Of Integration
Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ′= −∫ ′.
Basic Integral Formulas
Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2;.
Integrals ONE GREAT WORLD FOR ALL
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn.
Derivative Rules Cheat Sheet
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅.
Solved Determine which of the integrals can be found using
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax.
Integral cheat sheet Docsity
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value..
Basic Integral Rules
Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value.
Printable Integrals Table
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥.
Basic Rules Of Integration
′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant.
⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫Sum/Difference.
Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx.
Cheat Sheet For Integrals 1.
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2;